티스토리 뷰
[ 1. Controller 연습 ] (*****)
[ 1 - 1. @RequestMapping ]

[ 1 - 2. @RequestMapping(path = " ") ]

[ 1 - 3. @RequestMapping(path = { " " }, method = { " " } ) ]

[ 1 - 4. 단축형 - @GetMapping(path) / @PostMapping(path) ]
[ 1 - 5. 매개변수 있는 버전 ] (****)




[ 1 - 6. 매개변수가 Model인 버전 ] (****)

[ + 화면에서 Model 활용 ]

[ 1 - 7. @ModelAttribute(key) / Command Object ] (****)


[ + 화면에서 Model 사용 ]

[ 1 - 8. redirect: / RedirectAttributes 다른 곳으로 전송파라미터를 전달 ] (****)

[ 1 - 9. DispatcherServlet에 다음과 같은 객체 요구하기 ] ( 추천x )

[ 1 - 10. return 값으로 View를 지정해 주지 않을 경우 ]

더보기
[ + 코드 보기 ]
package org.zerock.myapp.controller;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributes;
import org.zerock.myapp.domain.SampleDTO;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import lombok.extern.log4j.Log4j2;
@Log4j2
@NoArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/sample2/") // 기본 URI ( base URI )
@Controller
public class SampleController2 {
// =======================================================
// 1. @RequestMapping or RequestMapping("")
// =======================================================
@RequestMapping
// + 이 경우에는 상세 URI가 지정되어 있지 않기에 기본 URI만 남게 된다.
// + 이 경우에는 http://localhost:8080/sample2/로 요청을 보내야 한다.
// + 실행하면 basic() invoked.가 찍히게 된다.
public String basic() {
log.trace("basic() invoked.");
return "sample";
} // basic
// =======================================================
// 2. @RequestMapping(path="", method=GET/POST)
// =======================================================
@RequestMapping(path="/basicGet", method=RequestMethod.GET)
// + 전체 URI = 기본 URI + 상세 URI -> /sample2//basicGet...? (x)
// + spring이 /sample2/basicGet로 처리해 준다.
public String basicGet() {
log.trace("basicGet() invoked.");
return "sample";
} // basicGet
// =======================================================
// 3. @RequestMapping(path="", method=GET/POST)
// =======================================================
@RequestMapping(
path={"/basicGet2", "/basicGet3", "/basicGet4"},
method= {RequestMethod.GET})
// + 위와 같이 배열 안에 { } 여러 개를 지정할 수 있다.
// + method에서도 { }를 통해서 GET방식과 POST 방식 모두 지정해 줄 수 있다.
public String basicGet2() {
log.trace("basicGet2() invoked.");
return "sample";
} // basicGet2
// =======================================================
@RequestMapping(
path= {"/basicGet70", "/basicGet80"},
method= {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST} // get 방식 , post 방식 둘다 요청 가능
) // http://localhost:8080/sample/basicGet
public String basicGet88(){
log.trace("basicGet88() invoked.");
return "sample";
} // basicGet88
// =======================================================
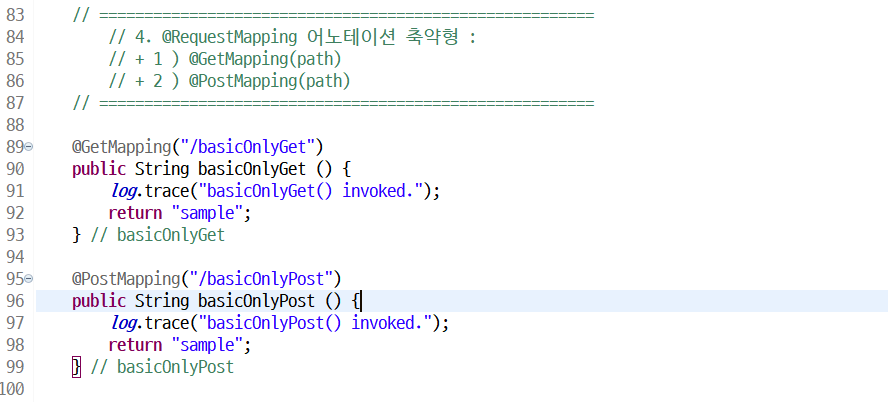
// 4. @RequestMapping 어노테이션 축약형 :
// + 1 ) @GetMapping(path)
// + 2 ) @PostMapping(path)
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/basicOnlyGet")
public String basicOnlyGet () {
log.trace("basicOnlyGet() invoked.");
return "sample";
} // basicOnlyGet
@PostMapping("/basicOnlyPost")
public String basicOnlyPost () {
log.trace("basicOnlyPost() invoked.");
return "sample";
} // basicOnlyPost
// =======================================================
// 5. @GetMapping(path) with DTO parameter ( 매개변수 o ) (***)
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/ex01")
public String ex01(SampleDTO dto) {
log.info("ex01(SampleDTO dto) invoked.");
log.info("\t + dto : {}", dto);
return "sample";
} // ex01
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/ex02")
public String ex02(String name, Integer age) {
log.info("ex02(SampleDTO dto) invoked.");
log.info("\t + name : {}, age : {}", name, age );
return "sample";
} // ex02
// =======================================================
// 6. @GetMapping(path) with 기본타입 parameter ( 매개변수 o ) (***)
// =======================================================
// + 기본타입의 경우 NULL은 받아 들일 수 없다.
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/ex03")
public String ex03 ( String name, int age ) {
log.info("ex03 ( String name, int age ) invoked.");
log.info("\t + name : {}, age : {}", name, age );
return "sample";
} // ex03
// =======================================================
// + 실제 전송파라미터의 이름이 헨들러의 매개변수의 이름과 다를 경우 (***)
// + 전송파라미터의 이름과 매개변수의 이름이 다르기에 받아오지 못한다.
// + 해결방법 : Spring이 제공하는 @ReauestParam 어노테이션을 이용하면,
// + 이름이 달라도 전송파라미터 값을 받을 수 있다.
// =======================================================
public String ex04 (
@RequestParam("name") String recvName,
@RequestParam("age") Integer currentAge ) {
log.info("ex04 ( recvName, currentAge ) invoked.");
log.info("\t + recvName : {}", recvName);
log.info("\t + currentAge : {}", currentAge);
return "sample";
} // ex04
// =======================================================
// 7. @GetMapping(path) with List객체 parameter ( 매개변수 o ) (****)
// =======================================================
// + @ResponseStatus는 에러가 나지 않아도 BadRequest로 보낼 수 있다.
// + @ResponseStatus는 에러가 나도 우리가 지정한대로 나가게 된다.
// + 그렇기에 사실 사용하지 않는 편이 좋을 수도 있다.
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) // Http Status code : 200, 404, 500
@GetMapping("/ex05List")
public String ex05List(
@RequestParam("id") List <String> id) // ArrayList로 만들어서 제공된다. (****)
// Integer [] id // 배열로도 얻을 수 있다. Arrays.toString
// + 배열 외의 다른 자료구조 타입으로, 여러 값을 가지는 전송파라미터를 필요로 하는 경우에는
// + 반드시 @RequestParam 어노테이션을 붙여야 한다. (******)
{
log.info("ex05List(id) invoked.");
log.info("\t + ids : {}", id);
log.info("\t + type : {}", id.getClass().getName());
return "sample";
} // ex05List
// =======================================================
// 8. @GetMapping(path) with 날짜형식의 parameter ( 매개변수 o ) (***)
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/ex06")
public String ex06(
// @DateTimeFormat(iso=ISO.DATE) Date date // OK
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") Date date ) {
log.info("\t + date {}", date);
log.info("\t + type : {}", date.getClass().getName());
return "sample";
} // ex06
// =======================================================
// + 전송파라미터의 경우에는 값이 String으로 받아지게 되는데
// + Spring에서 자동으로 변환해주게 된다. ( 형변환이 가능한 경우에만 )
// =======================================================
// =======================================================
// 9. @GetMapping(path) with Model타입의 parameter ( 매개변수 o ) (***)
// =======================================================
// + Model 타입의 객체는 MVC 패턴에서 말하는 Model 객체로
// + 비지니스 로직의 수행결과 데이터를 저장하는 '상자'와도 같은 역할을 수행한다.
// + 실제 타입을 출력하면, 바로 "Map" 객체임을 알 수 있다.
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/ex07")
public String ex07 ( String name, Integer age, Integer page ,Model model ) {
log.info("ex07(name, age, page, model) invoked.");
log.info("\t + name : {}, age : {} , page : {} ", name, age, page);
log.info("\t + model : {} ", model.getClass().getName());
// org.springframework.validation.support.BindingAwareModelMap
SampleDTO dto = new SampleDTO();
dto.setName(name);
dto.setAge(age);
// Model이란 상자 안에 비지니스 데이터(즉, 다양한 타입의 객체)를
// 저장할 때에는, 'addAttribute(key, value)'로 넣는다. (****)
// =======================================================
// + Model 상자에 addAttribute(key, value) 메소드를 이용해 객체를 저장한다는 의미는
// + 바로 Request Scope 공유영역에 저장된 key 이름으로 Value 객체를 바인딩 ( 즉, 공유속성 생성 )하는 것이다.
// + 때문에, EL 변수로 지정이 가능한 공유속성이 생기게 된다.
// =======================================================
model.addAttribute("sampleDto",dto);
model.addAttribute("page", page);
// Model을 활용하는 화면 불러오기
return "commandObject";
} // ex07
// =======================================================
// 10. @ModelAttribute(key) / Command Object (****)
// =======================================================
@PostMapping("/ex08")
// =======================================================
// + 전송파라미터를 객체를 통해서 수집하면, 이 객체를 스프링에서는 "Command Object"라고 부른다.
// + 스프링의 Command Object는 자동으로 View에게까지 전달된다. (****)
// =======================================================
// + Command Object로 들어오면 RequestScope에 자동으로 등록되게 되는데,
// + 이때 key의 이름은 Command Object 객체의 이름의 첫문자를 소문자로 변환해서 저장한다.
// =======================================================
// + 또한 @ModelAttribute 어노테이션을 사용하면,
// + 이것도 Model 상자에 들어와서 RequestScope에 들어가게 되어
// + view까지 전달할 수 있다.
// =======================================================
// + @ModelAttribute를 메소드 위에 붙이게 될 경우,
// + 매개변수를 담는 것이 아니라, 메소드의 리턴값을 RequestScope에 바인딩한다.
// + 즉, 이 경우에는 commandObject라는 뷰의 이름이 RequestScope에 바인딩된다.
// =======================================================
public String ex08 ( SampleDTO dto, @ModelAttribute("page") Integer page ) {
log.info("ex08(dto, page) invoked.");
log.info("\t + dto : {}", dto);
log.info("\t + page : {}", page);
return "commandObject";
} //ex08
// =======================================================
// + @ModelAttribute를 통해 화면에 전송하기
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/ex09")
public String ex09 (
@ModelAttribute("name") String name,
@ModelAttribute("age") Integer age,
@ModelAttribute("page") Integer page ) {
log.info("ex09(name, age, page) invoked.");
log.info("\t + name : {}, age : {} , page : {} ", name, age, page);
// Model을 활용하는 화면 불러오기
return "commandObject2";
} // ex09
// =======================================================
// 11. Predefined RedirectAttribute
// =======================================================
// =======================================================
// + To redirect a request into the other url
// =======================================================
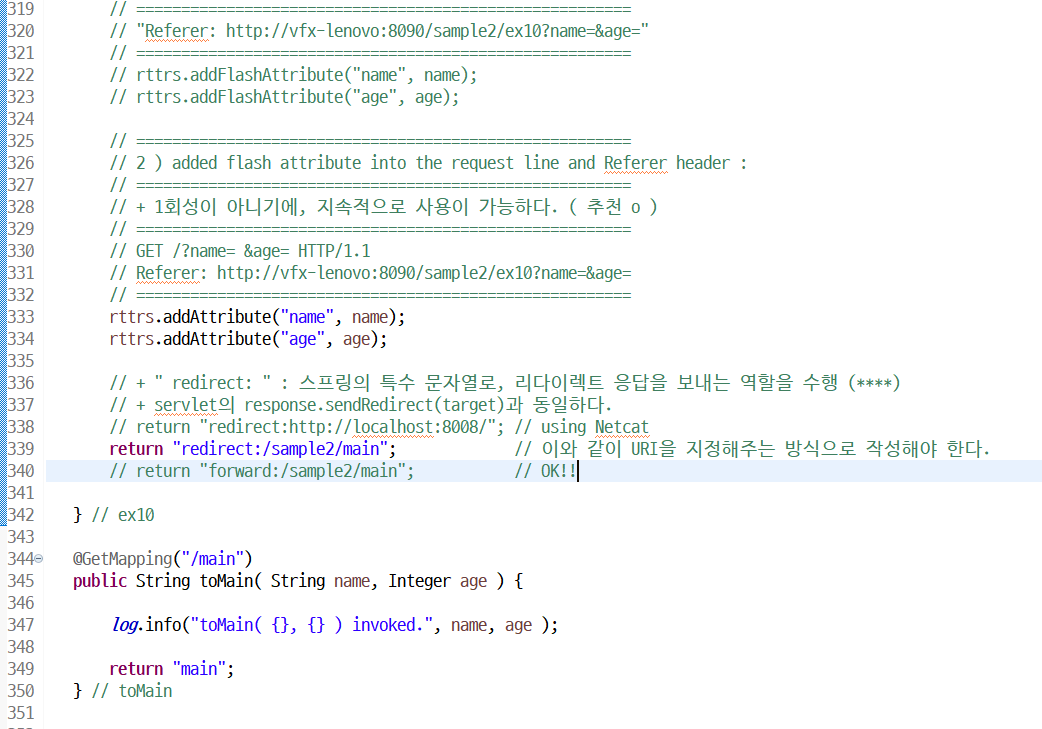
@GetMapping("/ex10")
// + 리다이렉트 되는 target url로 이동시, 같이 전달될 전송 파라미터가 필요할 경우
// + 이 RedirectAttributes 객체를 사용한다. ( Like Model 상자 )
public String ex10(String name, Integer age, RedirectAttributes rttrs) {
log.info("ex10(name, age, rttrs) invoked.");
log.info("\t + 1. rttrs : {}", rttrs);
log.info("\t + 1-2. rttrs type : {}", rttrs.getClass().getName());
// rttrs type : org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.RedirectAttributesModelMap
log.info("\t + 2. name : {}, age : {}", name, age);
// =======================================================
// 1 ) added flash attribute into header ( flash == 1회성 )
// =======================================================
// + 1번만 전달하고 없어져 버린다. ( 추천 x )
// + 이렇게 되면 전송된 값을 확실하게 확인할 수 없다.
// =======================================================
// "Referer: http://vfx-lenovo:8090/sample2/ex10?name=&age="
// =======================================================
// rttrs.addFlashAttribute("name", name);
// rttrs.addFlashAttribute("age", age);
// =======================================================
// 2 ) added flash attribute into the request line and Referer header :
// =======================================================
// + 1회성이 아니기에, 지속적으로 사용이 가능하다. ( 추천 o )
// =======================================================
// GET /?name= &age= HTTP/1.1
// Referer: http://vfx-lenovo:8090/sample2/ex10?name=&age=
// =======================================================
rttrs.addAttribute("name", name);
rttrs.addAttribute("age", age);
// + " redirect: " : 스프링의 특수 문자열로, 리다이렉트 응답을 보내는 역할을 수행 (****)
// + servlet의 response.sendRedirect(target)과 동일하다.
// return "redirect:http://localhost:8008/"; // using Netcat
return "redirect:/sample2/main"; // 이와 같이 URI을 지정해주는 방식으로 작성해야 한다.
// return "forward:/sample2/main"; // OK!!
} // ex10
@GetMapping("/main")
public String toMain( String name, Integer age ) {
log.info("toMain( {}, {} ) invoked.", name, age );
return "main";
} // toMain
// =======================================================
// 12. DispatcherServlet에 아래와 같은 객체도 요구할 수 있다.
// (1) request (2) response (3) session
// =======================================================
// + 하지만 이는 Spring의 MVC패턴을 어긋나게 하기에 추천하지 않는다.
// + 만약 이러한 방법으로 개발해야 된다면, 그냥 Servlet을 사용하는 것이 좋다.
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/core")
public String core(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session) {
log.info("core() invoked.");
log.info("\t + 1. request : {}", request);
log.info("\t + 2. response : {}", response);
log.info("\t + 3. session : {}", session);
return "sample";
} // core
// =======================================================
// 13. return 값을 주지 않는다면
// =======================================================
// + 만약 return 값으로 View를 지정해주지 않는다면,
// + 최종 View의 이름이 자동으로 기본 URI(/sample2) + 상세 URI(/returnVoid)로 지정된다.
// =======================================================
@GetMapping("/returnVoid")
public void returnVoid() {
log.info("returnVoid() invoked.");
// return View; 생략
// + View의 이름을 반환하지 않으면, 최종 View의 이름은 다음과 같이 결정된다. :
// + 최종 view 이름 = 기본 URI + 상세 URI => 예 : "/sample2/" + "/returnVoid" + ".jsp"
} // returnVoid
} // end class728x90
'KH 정보교육원 [ Java ]' 카테고리의 다른 글
| KH 113일차 - Spring MVC ( 파일 업로드 처리 ) (****) (0) | 2022.08.08 |
|---|---|
| KH 112일차 - Spring ( Controller ) (****) (0) | 2022.08.05 |
| KH 110일차 - Spring ( Spring MVC ) (****) (0) | 2022.08.03 |
| KH 109일차 - Spring ( mybatis-spring : mapper ) (******) (0) | 2022.08.02 |
| KH 108일차 - Spring ( MyBatis와 연동 ) (****) (0) | 2022.08.01 |
댓글
